Mitochondrial Health – A Closer Look
Published on 23 March, 2023
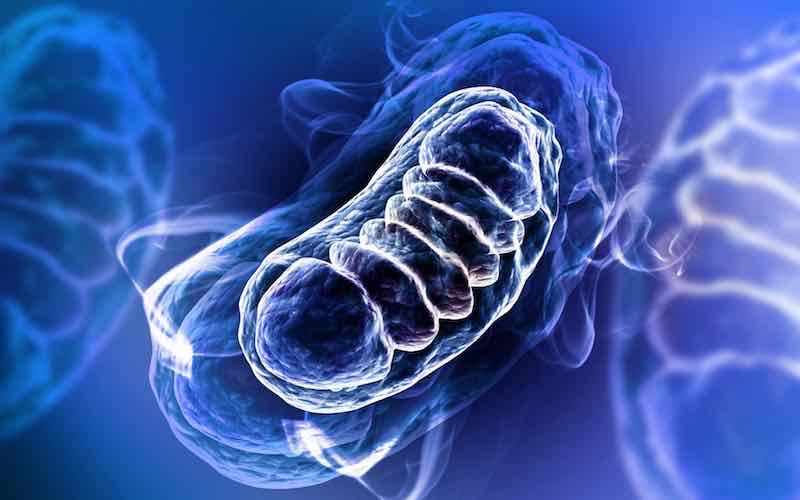
Mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including human cells. These tiny structures play a critical role in producing energy for the cell and have many other important benefits that help to keep the cell functioning optimally.
Here are 7 of the key benefits of mitochondria:
- Energy production: Mitochondria are responsible for generating most of the the cell’s energy supply through a process called cellular respiration. This process converts glucose and oxygen into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary source of energy for the cell.
- Heme biosynthesis: Heme carries iron in the red blood cells. The first step of heme synthesis is in the mitochondria. If this step doesn’t work because the mitochondria are dysfunctional, you cannot metabolise oxygen properly to make energy because your cells cannot carry iron.
- Steroid synthesis: Cholesterol is essential for all your steroid hormones, such as pregnenolone, progesterone, oestrogen and all the androgens. Cholesterol is cleaved in the mitochondria, which determines steroidogenesis. If the mitochondria are unable to function well, hormone production will be disrupted.
- Amino acid metabolism: The mitochondria are responsible for the metabolism of the non-essential amino acids (e.g., arginine, alanine, ornithine), which means that a lot of functions (including building DNA and RNA) will be dysregulated if the mitochondria are dysfunctional.
- Urea cycle: The urea cycle converts excess ammonia into urea in the mitochondria of liver cells. The urea forms, enters the blood stream, is filtered by the kidneys, and is then excreted in the urine. None of this will happen properly if the mitochondria are dysfunctional, and uric acid/ammonia will rise, which can be very serious.
- Regulation of cell death: Mitochondria play a key role in regulating cell death, or apoptosis. When the cell is damaged or no longer needed, mitochondria release signals that trigger the programmed death of the cell. This helps to prevent the spread of damaged cells, which can lead to disease or cancer.
- Antioxidant defence: Mitochondria are also involved in antioxidant defence, helping to protect the cell from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. This oxidative damage is associated with aging and a variety of diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
In conclusion, mitochondria play a vital role in maintaining the health and functioning of cells. From energy production to regulating cell death, and from antioxidant defence to hormone signalling, the benefits of mitochondria are numerous and essential for overall health.
- As part of AONM’s Mitochondrial Webinar Series

- Professor Brigitte Koening’s latest webinar addresses Advanced Mitochondrial Testing and Potential Therapies
- You can download the PDF of the Presentation HERE
- To learn more about mitochondria and the tests that AONM offer please see HERE
- Our Mitochondrial Testing Order Form can be found HERE
- References can be found HERE